Overview
The purpose of this document is guide you the usage of “lsof” command. LSOF
command is utilized to know the “LiSt of Open Files” by processes.
As we are aware Linux / Unix considers everything as files such as (pipes,
sockets, devices, etc.).
This command is also useful when you want to unmount filesystem
and but you are unable to unmount filesystem or process is running is memory.
It is also useful wherein a file is deleted and file is resident in memory. lsof command will help us to find out
files that are currently in use and its current state of such files.
Applies To
Tested on RHEL 7, CentOS 7.
Pre-Requisites
·
lsof package is
installed
Install Package
LSOF package
is installed by default in when you install operating system, in order to
install the package if the package is not installed run the command;
yum install -y
lsof
Validate Package Installation
To verify the package
installation status, run the command;
rpm -qa | grep
lsof
First we need to understand
the output format of lsof command ,
below will give you a brief insight to different sections.
FD and Types are the that we will focus upon,
reset of the fields are self-explanatory.
File Descriptor Table
FD stands for File Descriptor
and it has different values are listed when you the command. A few of them are
listed below.
File Descriptor
|
Purpose
|
cwd
|
current working directory
|
rtd
|
root directory
|
pd
|
parent directory
|
txt
|
program text (code and data)
|
mem
|
memory-mapped file
|
mmap
|
Memory mapped device
|
number character
|
The character after the number i.e ‘1u’,
represents the mode in which the file is opened.
r for read, w for
write, u for read and write.
|
Type Descriptor Table
Specifies the type of the
file. Some of the values of TYPEs are:
Type Descriptor
|
Type of File
|
REG
|
Regular File
|
DIR
|
Directory
|
FIFO
|
First In First Out
|
CHR
|
Character special file
|
List of Opened Files – User
To list the files opened by a user, run the command;
lsof -u chrony
Note: To
list of files that are open for multiple users run the command lsof -u mysql -u postfix.
List of Opened Files – Exclude User
To list of open files
excluding a user(s), execute with option “-u”
and “^” along with the user, run the
command;
lsof -u^root
Note: To exclude
results of additional users, run the command lsof -u ^mysql -u ^chrony
-u ^dbus.
List of Opened Files – Directory
To list the files that are
opened in a specific directory, run the command;
lsof +D
/var/log/
List of Open Files – By Process Name Starting With
List the files that are open
by process name(s) starting with, run the command;
lsof -c mysql
Note: To
list of files that are open for multiple process names run the command lsof -c mysql -c systemd.
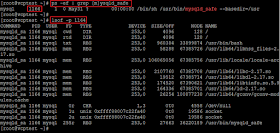
List of Open Files – By PID
To list files that are open
by process id, run the command;
ps -ef | grep [m]ysqld_safe
lsof -p 1164
List Processes – By Specific File
To list the processes
associated with a specific file, run the command;
lsof /var/log/Xorg.0.log
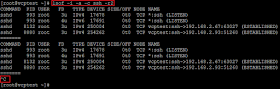
List all Network Connections
List all the network
connections listening and established, run the command;
lsof -i
List Network Connections – Only IPv4
List all IPv4 network
connections listening and established, run the command;
lsof
-i 4
List Network Connections – Only IPv6
List all IPv6 network
connections listening and established, run the command;
lsof
-i 6
List Network Connections – TCP Port Range
List all the network
connections listening and established for TCP
port range, run the command;
lsof
-i TCP:1-1024
List Network Connections – UDP Port Range
List all the network
connections listening and established for UDP
port range, run the command;
lsof
-i UDP:1-1024
Find Processes Running – Specific Port
To list the process running on
a specific port, run the command;
lsof
-i :22
List all network files in use by a specific process
To list all the network files
which is being used by a process; run the command
lsof -i -a -p
8132 or lsof -i -a -c ssh
List of Files in Repeat Mode
To list the files that are
opened in repeat mode (loop until no
files are open) “+” is prefixed before
command “repeat option r” and
refresh the output every 2 seconds, run the command;
lsof -i -a -c
ssh +r2
Note: Each cycle
output is separated by “=======”
List of Files in Repeat Mode
To list the files that are
opened in repeat mode (loop until
interrupt “ctrl +c”) “-” is prefixed before
command “repeat option r” and
refresh the output every 5 seconds, run the command;
lsof -i -a -c
ssh -r2
Note: Each cycle
output is separated by “=======”
List all NFS files
To list Network File System files in use, for a user. Run the
command;
lsof -N -u root -a
Note: In this
case there is NFS is not utilized.
Kill All Process – Particular User
To list and kill all the process of a particular user; “-t” option will list only the process id of the user, run
the command;
lsof -t -u postfix
kill -9 `lsof -t -u postfix`
SlideShare Information
Step by step guide is uploaded.













No comments:
Post a Comment